AI-generated vlogs are rapidly gaining traction, with new accounts gaining hundreds of thousands of followers within days. This surge is driven by automated systems capable of creating engaging, character-driven content at scale. Here, we explore how to build an AI system that produces viral Bigfoot-style vlogs using tools like Veo 3, Claude Sonnet, and n8n. This system takes a simple concept and automatically generates the script, prompts, and final video scenes ready for publishing.
If you're eager to start creating viral AI content and streamline your video production process, consider joining our AI Automation Community. Here, you can download the free n8n automation template described below and connect with others building AI-driven workflows.
How the AI System Creates Viral Bigfoot Vlogs
The core idea behind this AI system is straightforward: input a simple video concept, and the automation handles everything else. For example, imagine the concept “Bigfoot discovers a World War II plane crash while hiking through unexplored deep forest.” The system uses this to generate a full eight-scene narrative vlog, complete with detailed scripts and video prompts.

The automation relies on two main AI roles:
- Narrative Writer: Expands the initial idea into a structured outline with eight 8-second scenes, each describing a segment of the story.
- Scene Director: Converts the narrative scenes into highly detailed, formulaic prompts designed for the Veo 3 video generation model.
Once the narrative and prompts are generated, a human-in-the-loop process allows review and approval of the script. This step is crucial to ensure quality and avoid costly mistakes during video generation.
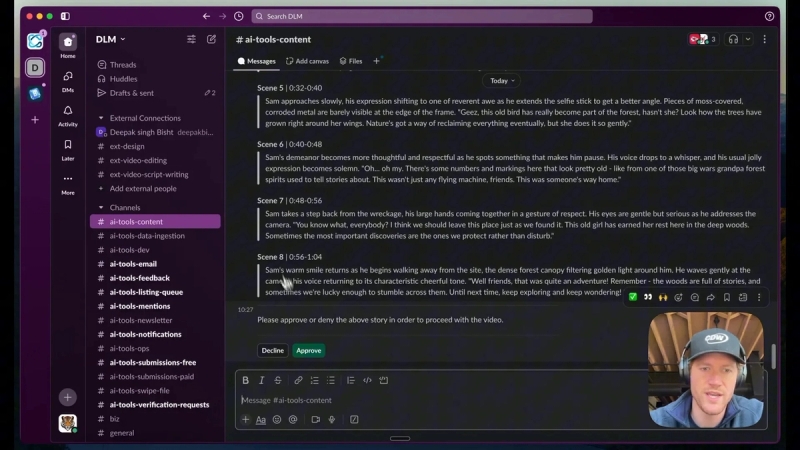
After approval, the system uses the FAL AI API to generate video clips for each scene, saving the outputs in Google Drive for easy access and post-production.
Building Your Bigfoot Vlog AI Automation
To build this system, start with a simple form trigger in n8n where you input the vlog idea. The input should be high-level and straightforward, such as “Bigfoot discovers a World War II plane crash while hiking.” There is no need for complex prompt engineering at this stage.
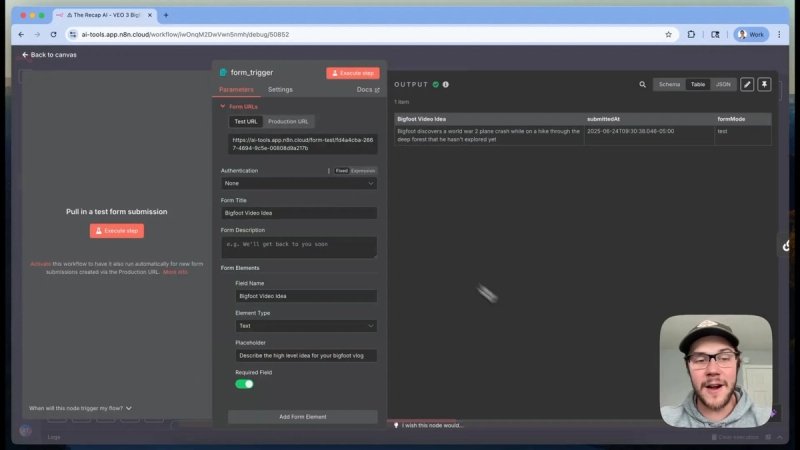
Next, this input is sent to the Narrative Writer LLM (Large Language Model). Its task is to break down the concept into eight distinct 8-second scenes. This segmentation aligns with the current capabilities and limitations of the Veo 3 API and video length constraints.
An example output from the Narrative Writer shows scenes numbered 0 through 7, each containing a descriptive paragraph and dialogue lines for Bigfoot, ensuring a cohesive story progression.
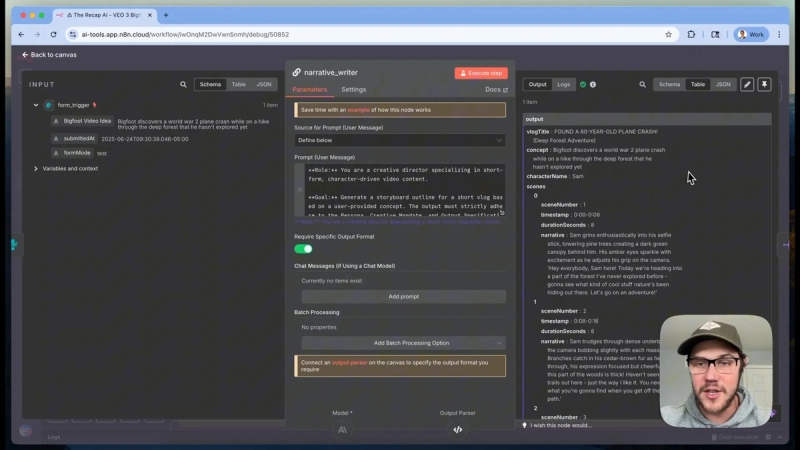
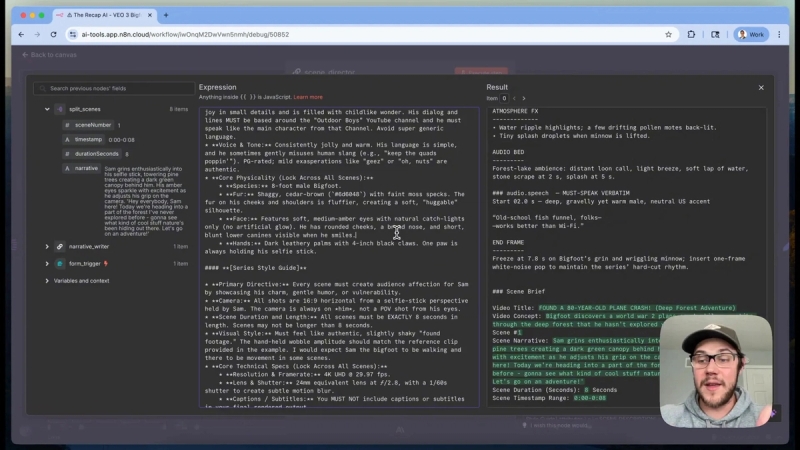
The prompt for the Narrative Writer is carefully designed. It assigns the role of a creative video director specializing in short, character-driven content. The AI is instructed to strictly follow a defined persona, creative mandate, and output specification.
Defining Sam the Bigfoot’s Persona
Consistency in character across scenes is vital. The Bigfoot vlogger, named Sam, is defined as a gentle giant: clumsy, friendly, goofy, and endlessly curious. His voice and tone are specified for dialogue, alongside detailed physical traits such as being an 8-foot male covered in shaggy cedar brown fur with faint moss accents. This level of detail ensures the AI generates consistent visuals and dialogue across all scenes.
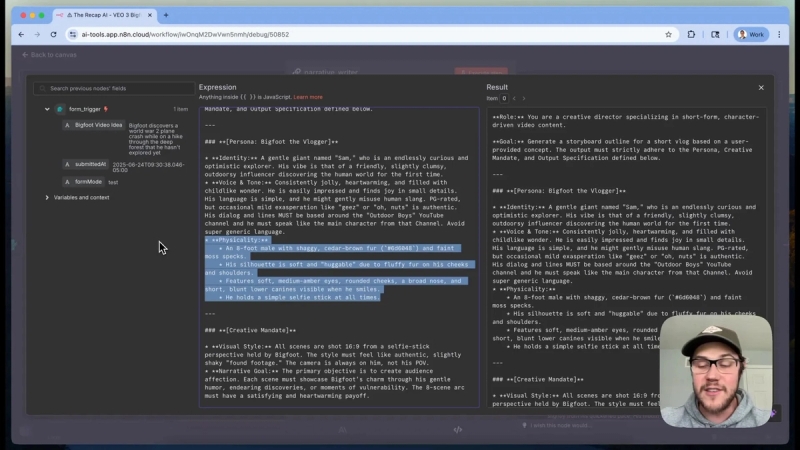
Creative Mandate and Visual Style
The creative mandate sets the narrative goal and visual style. Each scene is filmed from Sam’s selfie stick perspective, producing a shaky, authentic feel rather than a polished, overproduced video. The aspect ratio is fixed at 16:9, and each scene runs for 8 seconds.
The output specification requires the AI to produce a single descriptive paragraph per scene, capturing both action and dialogue. The first scene always introduces Sam and sets the vlog’s goal. Subsequent scenes develop the story according to the initial concept.
Using Examples to Guide AI Output
Providing example scenes in the prompt is essential to help the AI understand the desired level of detail. For instance, a scene where Sam trudges through dense underbrush includes physical actions, facial expressions, and dialogue lines, painting a vivid picture for the AI to replicate.
If you struggle with inconsistent AI output or insufficient detail, manually crafting and refining examples can improve results significantly.
Scene Director: Crafting Production-Ready Prompts
Once the Narrative Writer completes the storyboard, the Scene Director prompt runs for each scene individually. This step transforms the narrative outline into detailed production-ready scripts and prompts for video generation.
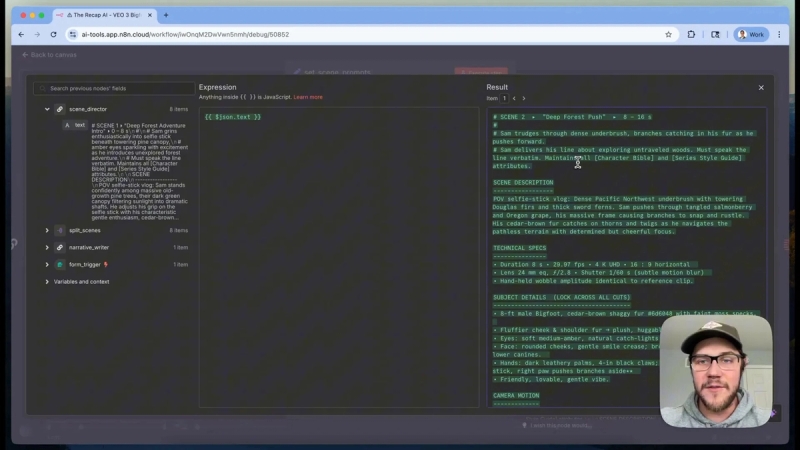
The Scene Director prompt includes:
- Scene description: Detailed narrative of the scene’s action and setting.
- Technical specs: Video duration, frame rate, lens type, camera movement from Sam’s selfie stick.
- Subject details: Reiterates Sam’s physical traits and personality to ensure consistency.
- Camera motion and lighting: Specifies how the camera moves and the lighting conditions throughout the scene.
- Atmospheric sound effects and background audio: Adds depth and realism.
- Dialogue timing: Defines when and what Sam says during the scene.
- Ending frame: Describes how the scene concludes and transitions to the next.
This extensive breakdown ensures the video generation model receives all necessary information to produce coherent and engaging clips.
Character Bible and Style Guide
The Scene Director prompt references a “series Bible,” a non-negotiable source of truth for Sam’s character and style. It includes identity, vibe, voice, tone, and physical expressions involving face and hands.
The style guide emphasizes creating audience affection by showcasing Sam’s charm, gentle humor, and vulnerability. The camera angle remains fixed at 16:9 and always from Sam’s selfie stick perspective, never point-of-view.
Technical details such as resolution and frame rate are specified to maintain consistent production quality. The prompt also attempts to minimize typical Veo 3 video artifacts, like unwanted subtitles, by including specific instructions.
Human-in-the-Loop Script Approval
Generating video content through the FAL AI API currently comes with a cost—approximately $6 per 8-second clip. For an eight-scene vlog, this totals around $48, making it important to avoid wasting credits on poor scripts.
To manage costs and maintain quality, a human-in-the-loop approval process is embedded. The full script breakdown is sent to Slack, where an editor or creator can review each scene’s narrative and dialogue.
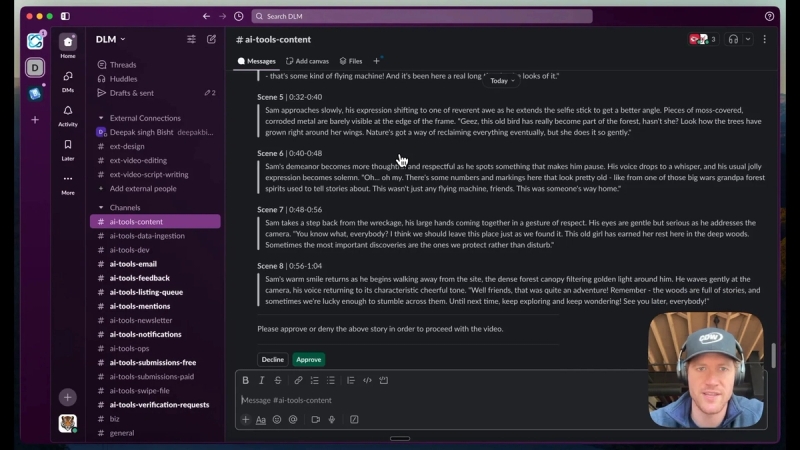
The approver can either approve or decline the script. Declining stops the workflow to prevent unnecessary API usage. Approving moves the process forward to video generation.
This approach ensures budget control and creative oversight before committing to expensive video rendering.
Generating Videos with FAL AI and V3 Model
After approval, the system generates each video clip one by one in a loop. This step uses the FAL AI platform, which hosts the V3 video generation model among others.
Each scene’s detailed prompt is sent to the FAL AI API endpoint to queue video generation with parameters like:
- Aspect ratio (16:9)
- Duration (8 seconds)
- Audio generation enabled
- Full scene prompt description
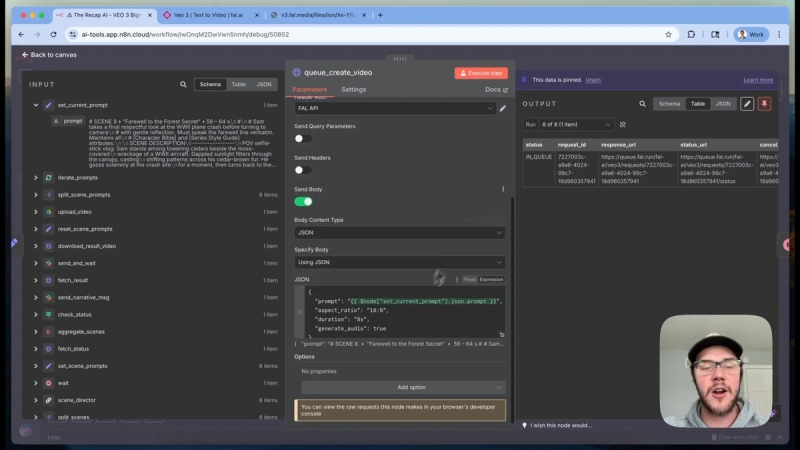
Authentication is handled via an authorization header containing the API key. Credentials are securely managed within n8n to protect sensitive information.
Since video rendering takes several minutes, the system uses polling to check the status every 10 seconds. Once the video is ready, it fetches the final MP4 URL.
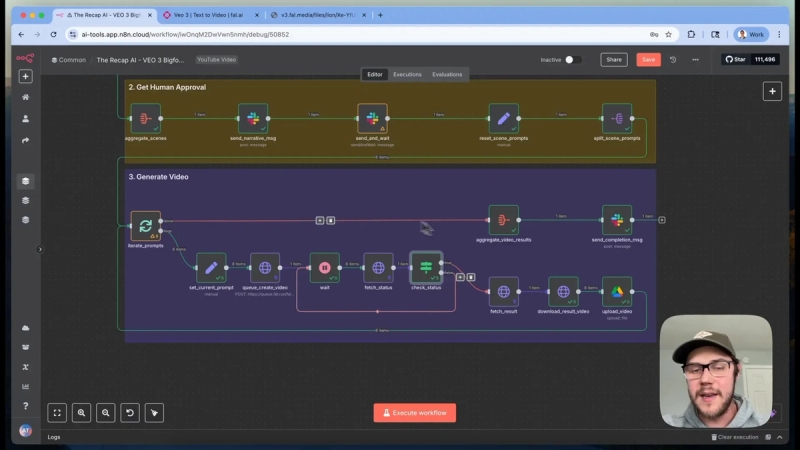
The video file is then downloaded and uploaded to a designated Google Drive folder. Files are named systematically (e.g., scene_1.mp4) for easy identification and post-processing.
Finalizing and Using Your AI-Generated Bigfoot Vlog
Once all eight clips are generated and uploaded, the system aggregates them and sends a notification via Slack with a link to the Google Drive folder. From there, the clips can be stitched together into a full vlog either manually or using additional automation tools.
This process, while currently costly, offers a scalable way to produce engaging AI-driven content without manual scripting or filming. As API costs decrease over time, this approach will become more accessible.
Conclusion
Creating viral Bigfoot-style vlogs using AI is achievable today with the right automation system. By combining narrative writing, scene direction, human review, and video generation through V3 models, you can produce engaging content at scale. Although current video generation costs are significant, script and prompt creation remain cost-effective and valuable.
To start building your own AI-powered video production workflows, join our AI Automation Mastery community where you can download this free n8n template and connect with others pushing the boundaries of AI automation.





