Building websites often means repeated manual tasks: research, content extraction, writing a PRD, and then writing all the code. This agent reduces the manual work by automating the entire process.
If you want to get the exact n8n template and prompts I used, join our AI Automation Community to grab the free n8n template and follow along.
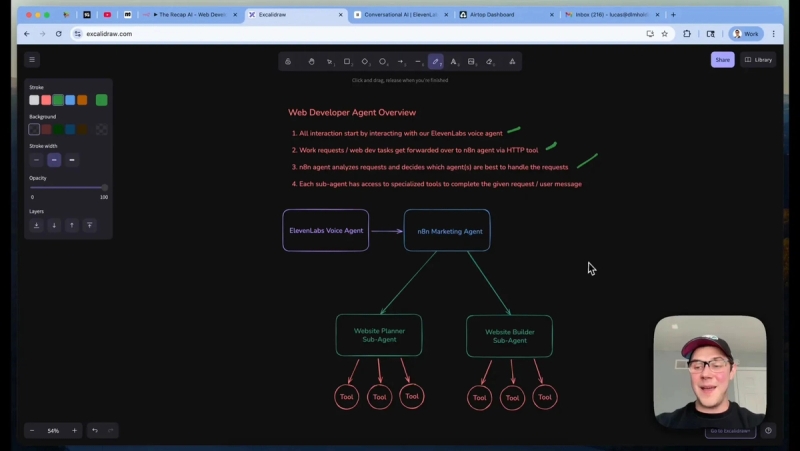
System overview: components and responsibilities
The system has four main parts:
- ElevenLabs voice agent — user entry point, handles conversation and decides when to forward web development requests.
- Custom webhook tool — forwards the user message from ElevenLabs into n8n.
- n8n parent agent (AI web developer) — router/orchestrator that decides which sub agent handles the task.
- Two n8n sub-agents — Website Planner (scrape + PRD) and Lovable Browser (Airtop-powered browser automation to create or edit sites).
Design principle: agent orchestrator pattern
Instead of creating a single agent with dozens of tools, I split responsibilities across a parent agent and small, focused sub agents. The parent agent only decides which sub-agent to call. Each sub-agent owns its playbook and tools. This reduces complexity and makes the system more reliable.
Benefits of splitting agents
- Smaller system prompts per agent
- Less chance of tool conflicts or hallucination
- Clear responsibilities make debugging easier
Step 1: Build the ElevenLabs voice agent
The voice agent is the conversation layer. It handles back-and-forth with the user and decides when to forward requests to the n8n backend using a custom webhook tool.
Key configuration points
- Choose a voice, set the first greeting, and paste a robust system prompt.
- System prompt must define personality, goal, guardrails, and when to call the webhook tool.
- Use a single custom tool named consistently with your webhook handler, for example forward_webdev_request or webdev_request.
Metaprompting: shortcut to a great system prompt
I used metaprompting: paste the ElevenLabs docs into an LLM (Claude or ChatGPT) and ask it to draft a system prompt. That gives a solid starting prompt that you can edit and tighten. The output should include a strategic decision-making section that clearly lists the conditions for forwarding to the webhook tool, such as:
- New website creation
- Existing website scraping or analysis
- Website editing tasks
- Technical planning or PRD generation
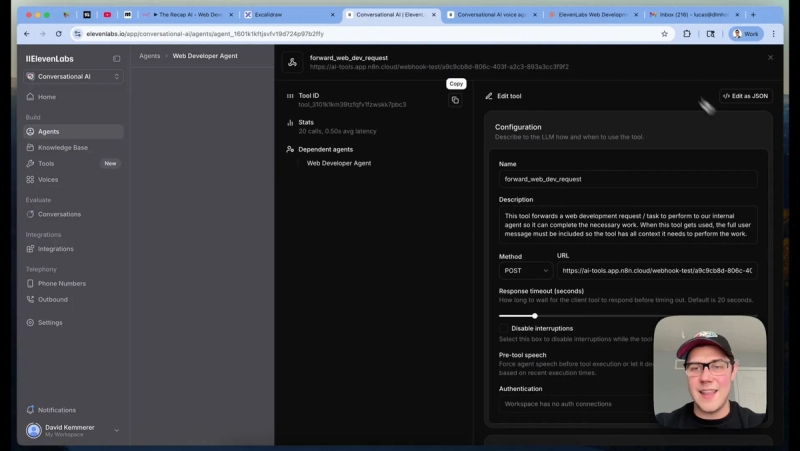
Step 2: Create the webhook tool in ElevenLabs
Set up a webhook tool that posts to an n8n webhook URL. Configure the HTTP method as POST and define a single body field named user_request_message with value type LLM prompt. This ensures the entire user utterance is forwarded to n8n.
Step 3: Parent AI web developer agent in n8n
In n8n, implement a parent agent workflow that receives the webhook or chat trigger and forwards the user message into an AI node acting as the orchestrator. The orchestrator's job is to:
- Use the think tool as a scratch pad to plan routing
- Decide if Website Planner or Lovable Browser should be called
- Return an immediate HTTP response to avoid webhook timeouts
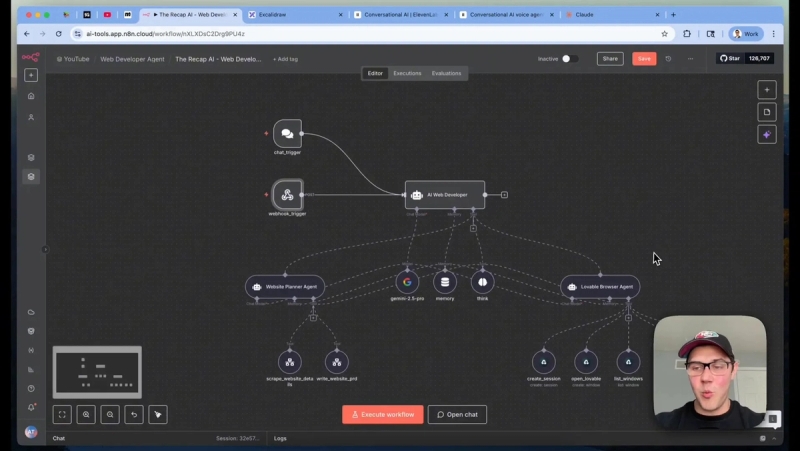
Webhooks often timeout if the process takes too long. I set n8n to respond immediately and do the heavy work asynchronously. That prevents the voice agent from erroring out while n8n builds the site in the background.
Step 4: Website Planner sub-agent
This agent handles research and planning. It has two core tools:
- Scrape website details — uses Firecrawl to map and scrape the site into clean markdown.
- Write PRD — takes the scraped markdown and generates a product requirements document the builder agent can use.
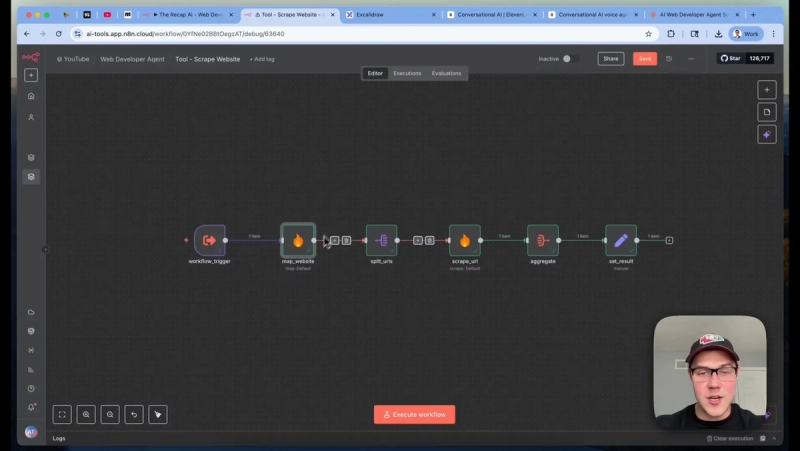
Scraping with FireCrawl
I use FireCrawl's map endpoint to get all page URLs, then scrape each URL and aggregate results into a single markdown blob. Be sure to include business-critical fields like address, phone, hours, and service descriptions so the PRD does not hallucinate facts.
Generating a PRD
The PRD workflow is a short n8n chain that loads the scraped content, runs a prompt in an LLM node, and outputs a structured PRD. The PRD should include conversion-focused recommendations and a clear brief that the builder can paste into Lovable.
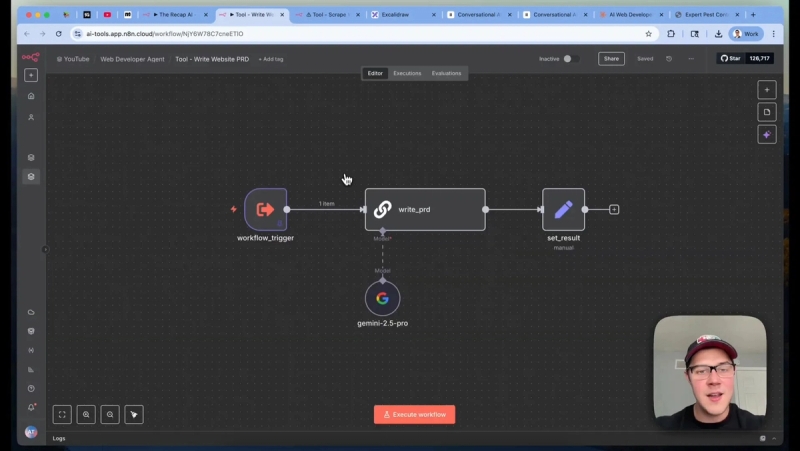
Step 5: Lovable Browser sub-agent with Airtop
Lovable has no public API, so I control the browser via Airtop. Airtop spins up a cloud Chrome instance and accepts instructions like create session, open window, type into an element, and list windows. The lovable browser sub-agent coordinates those calls.
Airtop tools:
- Create a session — spin up a new browser instance and save the session ID to memory.
- Open a window — navigate to lovable.dev and load the profile that is already logged in.
- Create website — type the PRD into the main text area and submit the form to start site generation.
- List windows — once the site generates, grab the project URL from the open windows and persist it.
- Edit website — when the user asks for updates, go to the project's edit textbox and type the feedback, then submit.
Profiles to avoid auth issues
Airtop profiles allow you to persist a logged-in session for Lovable. Create a profile with your Lovable account so the automated browser does not hit login walls. This keeps the workflow stable and secure.
Tool design tips
- Use clear element descriptions for Airtop's type operations, and instruct the tool to strip newline characters that could trigger early submission.
- Separate create and edit tools for reliability. That reduces conditional logic and keeps each tool focused.
- Expose a live view URL for debugging so you can watch what the browser does during execution.
Memory, think tool, and reliability
Memory is crucial. I group conversation history by a daily key so the agent behaves like a colleague you work with during a day. The think tool acts as an internal scratch pad. Require the think tool to run before routing so the agent can plan its steps and list tool calls.
Testing and debugging
When you test, use the respond-immediately pattern and watch the Airtop live view. If something breaks, check the list windows output to see what URL the browser is on. That gives a quick way to detect stuck states or unexpected pages.
Practical example: redesign request flow
Here is the end-to-end flow for a redesign request:
- User speaks to the voice agent asking for a PRD or a site build.
- ElevenLabs decides this is a webdev request and calls the webhook with the full user message.
- n8n parent agent loads the message, uses the think tool to plan, and routes to Website Planner to scrape the existing site.
- Website Planner scrapes content and generates a PRD using an LLM.
- Parent agent routes to Lovable Browser agent which spins up Airtop, opens Lovable, pastes the PRD, and submits to create the site.
- Lovable generates a draft site. The agent captures the project URL via list windows and saves it for future edits.
Next Steps
This AI web developer agent is a practical way to automate the repetitive parts of website builds: research, PRD drafting, and the first pass at implementation. Start by building the ElevenLabs voice agent and webhook, then implement the parent orchestrator in n8n, and finally add the planner and Airtop-driven builder. Test with a single site before scaling to multiple profiles.
Ready to try the exact template and join builders doing the same work? Join the AI Automation Mastery community to download the free n8n workflow and templates and start building today.





