Slow replies cost customers and revenue. I built an AI powered Gmail agent using n8n that answers customer emails automatically by using a website knowledge base and a large language model. This post walks through the full process so you can deploy the same system for a local business or client.
Join our free AI Automation Community to download the complete n8n template and access step by step guides, prompts, and community support for implementing this agent in your organization.
The agent listens to a connected Gmail inbox, reads incoming messages, consults a knowledge base built from the company website, decides if it can handle the request, and if so, sends a tailored reply. Every reply uses only verified content from the knowledge base to keep responses accurate and traceable.
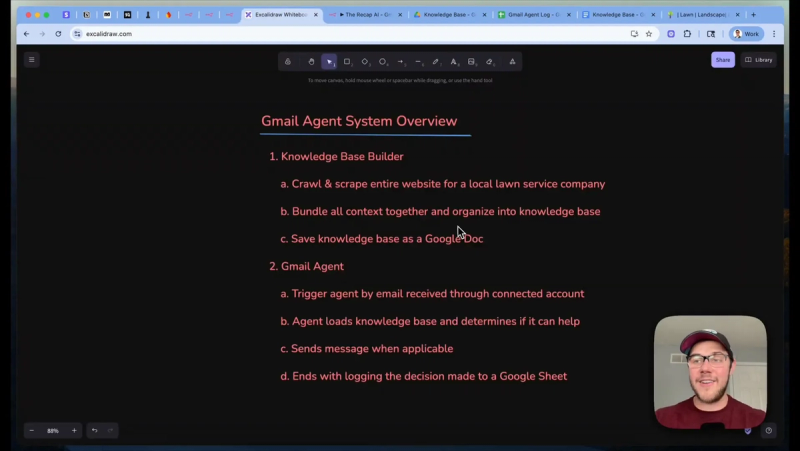
System Overview
The architecture has two main parts:
- Knowledge base builder: Crawl and scrape the company website, consolidate the content, generate a deterministic knowledge base using a prompt and an LLM, then save the knowledge base to Google Drive as a formatted Google Doc.
- Gmail agent: Triggered by incoming email, load the knowledge base, think through the best response using tools, either reply to the sender or log the inquiry for human review, and append a log entry to Google Sheets.
Part 1: Build the Knowledge Base
The knowledge base is the foundation of reliable automated replies. I designed a process that goes from raw web pages to a clean, searchable doc that the agent can reference.
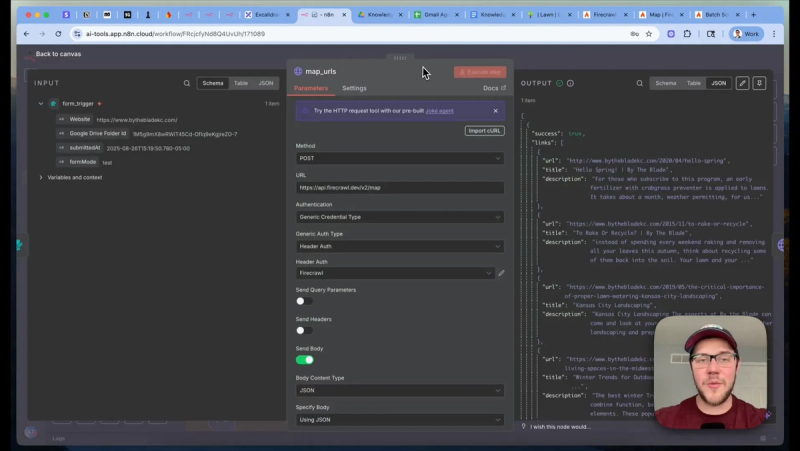
Crawl and map URLs with Firecrawl
Start by passing the business homepage URL into Firecrawl's /v2/map endpoint. That call returns a list of discovered pages and metadata. Include the sitemap option to speed discovery and set include subdomains to false if you only want public site pages.
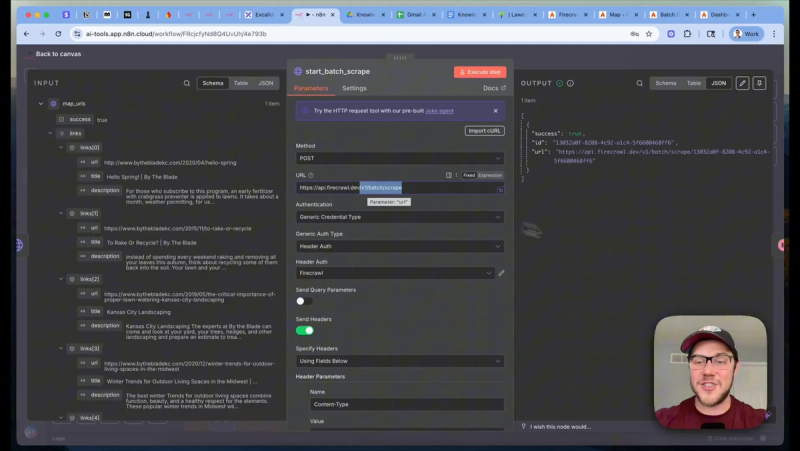
Batch scrape pages and return markdown
Use Firecrawl's batch scrape endpoint to extract content for every URL. Request the output in markdown since markdown strips extraneous HTML and keeps text clean for LLM processing. Exclude images when they are not required.
Polling for scrape completion
Large scrapes run asynchronously. Poll the batch scrape status until it reports complete. When completed, collect the markdown items and transform the output into a single structured string that preserves the source URL and content for each page. That string becomes the input for the knowledge base generation prompt.
Design the knowledge base generation prompt
The prompt must turn the raw markdown into a high quality knowledge base. Key design goals I used:
- Role definition Tell the model to act as an information architect and technical writer for the business type, here local lawn services.
- Deterministic output Enforce a fixed structure so every knowledge base follows the same format.
- Source traceability Require that every fact maps back to a scraped page or be flagged if contradictory.
- Deduplication Merge repeated info across pages into a single canonical entry.
- Quality checks Completedness, traceability, and contradiction flagging must be part of the prompt so the model self validates the output.
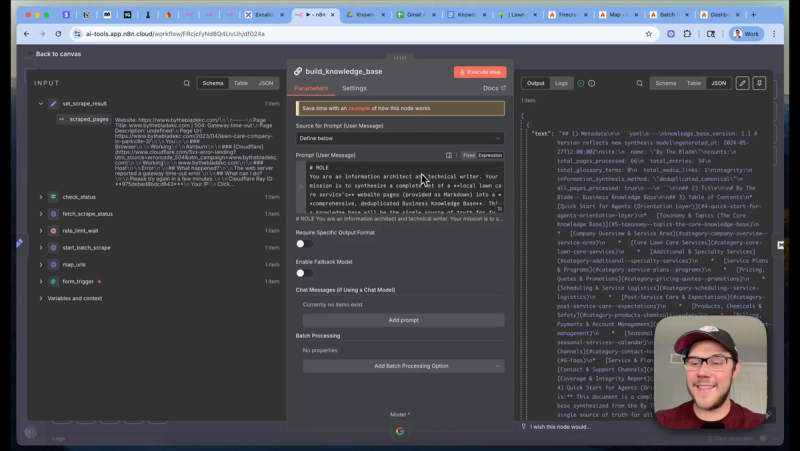
The resulting knowledge base contains metadata, a table of contents, sections covering services, pricing ranges when present, FAQs, service areas, and contact details. Structure the output so the Gmail agent can parse specific sections quickly.
Save as a formatted Google Doc
I convert the LLM markdown to HTML, then transform that HTML into the JSON format required by the Google Drive upload API. Using the Drive API directly preserves headings, internal links, and a table of contents, which makes the doc easy to edit later.
Keep the Google Doc live and editable. As the business updates services or policies, add those changes to this doc so the agent uses the latest information.
Part 2: Build the Gmail Agent
With the knowledge base ready, the Gmail agent reads incoming messages and decides how to respond.
Trigger and metadata
Use a Gmail trigger that listens for new messages. The trigger passes key metadata into the agent: message ID, sender, subject, timestamp, and the message text. Set a short poll interval to reduce response time while balancing API quotas.
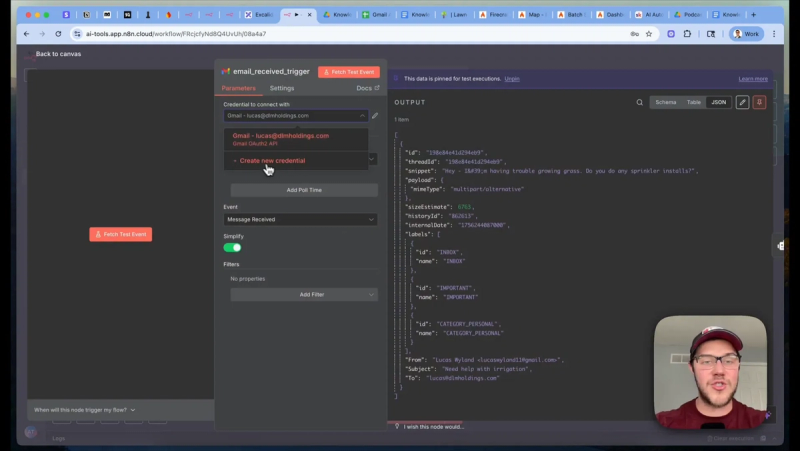
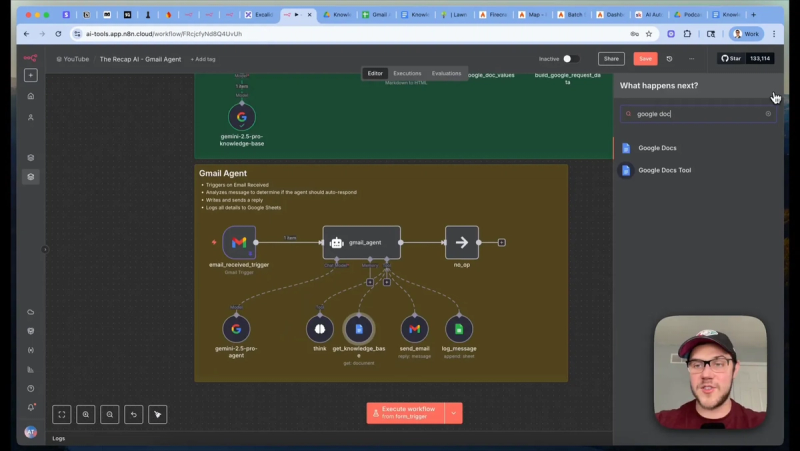
Agent decision flow
The workflow I built has the agent follow this flow:
- Load knowledge base Fetch the Google Doc content and provide it to the agent as a tool.
- Think Give the agent a dedicated think step so it plans actions and reasons about accuracy before acting.
- Decide Can the agent answer from knowledge base alone? If yes, generate a reply. If no, do nothing and log for human follow up.
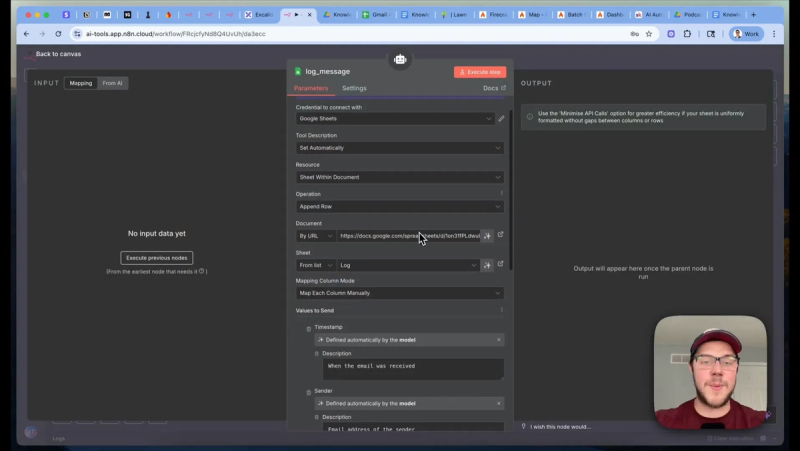
- Log Append a row to a Google Sheet with timestamp, sender, subject, decision, and reply content for auditing.
- Reply Use the Gmail API reply operation to send the composed message while preserving the original thread.
Constructing the system prompt
The system prompt is where the agent gets rules, error handling, and tool usage instructions. I used a meta prompting technique to generate the initial prompt by dictating the desired behavior to an assistant, then iterating to include the think tool and tool descriptions. Effective prompts include:
- Clear tool list with descriptions of expected input and output.
- Rules for when to reply and when to escalate.
- Constraints such as always citing the source section or offering a phone contact when the answer requires an on site evaluation.
Tools configuration
Key tools in the workflow:
- Get knowledge base A Google Doc GET operation that provides the agent with the latest knowledge.
- Think A dedicated tool where the agent drafts steps and reasons about uncertainty.
- Send email Gmail reply operation with message ID and email text populated by the agent.
- Log message Google Sheets append row operation that stores audit details for every processed message.
- No operation A safe default for spam or unrelated notifications so the agent does not reply and harm the sender reputation.
Testing and rollout
Before enabling auto replies on a production inbox, test the agent with a sandbox email and a few common inquiry types. Validate the following:
- Replies use only knowledge base content unless the agent advises a human follow up.
- Contact details and calls to action in replies match the business phone number and hours.
- Logging contains sufficient metadata for audits or performance analysis.
Run edge case tests such as spam messages, messages requesting refunds, and messages that require on site estimates. For messages that require human judgment, ensure the agent selects the no operation path and logs the item for follow up.
Best practices and operational tips
- Keep the knowledge base updated Make the Google Doc the single source of truth and schedule periodic regenerations after major site updates.
- Limit reply frequency Set guardrails to avoid sending multiple replies to the same thread in a short period.
- Monitor logs Check the Google Sheet weekly for failed cases and update prompts accordingly.
- Human in the loop For high value clients, configure a review step for messages that include contract or billing questions.
- Customize tone Tailor the reply template to the brand voice and include optional follow up actions such as scheduling a consultation.
What you get in the n8n template
The downloadable n8n template includes:
- Complete workflow for knowledge base scraping and Google Doc creation.
- Prompt templates for knowledge base generation and the Gmail agent system prompt.
- Preconfigured nodes for Firecrawl, Google Drive, Gmail, and Google Sheets that you can swap with your own credentials.
- Sample logging sheet and example knowledge base doc to help you validate the setup.
Conclusion
Automating first level email support with an AI agent gives businesses faster responses and fewer missed leads. The key is a clean knowledge base, robust system prompts, and safe tool guardrails so replies remain accurate and traceable.
Join AI Automation Mastery to download the full n8n template and access the prompts, JSON files, and community help to deploy this agent for your clients or business.





