This guide walks through the full build: scraping local events, turning the data into a narrated script with audio tags, and generating final audio using ElevenLabs v3. You will see each step, key decisions, and screenshots at critical moments so you can replicate the system.
Want to create a daily local podcast without a host, editor, or research team? Join our AI Automation Community to get the template and automation assets used in this tutorial.
Overview: What this system does
This pipeline automates the research, writing, and narration of a short local podcast episode. At a high level the flow is:
- Scrape local news and events using a curated Google News query converted to an RSS/JSON feed.
- Fetch and clean full article content with a web scraping service that returns Markdown ready for an LLM.
- Prompt an LLM to write a voice script that includes ElevenLabs v3 audio tags for emotion, pacing, and sound effects.
- Send the tagged script to ElevenLabs text-to-speech API to create a final audio file.
The system runs in an automation tool (n8n). You will use RSS generation, Firecrawl batch scraping, and ElevenLabs API calls. The result is a fully automated episode that can be published or integrated into other workflows.
What you will learn
- How to create a reliable feed of local events and news.
- How to convert multiple web pages into LLM-ready content.
- How to use ElevenLabs v3 audio tags to control narrator tone and effects.
- How to call ElevenLabs API to produce high-quality podcast audio files.
- Basic production tips and options for scaling the system.
Step 1: Source and gather local event data
Start by building a search that returns the local events you want to cover. A focused Google News query for the city and the keyword “events” produces a consistent list of articles and event pages to scrape. Convert that query into a machine-friendly feed using an RSS generator like rss.app. The feed gives you an accessible JSON endpoint containing article links and summaries.
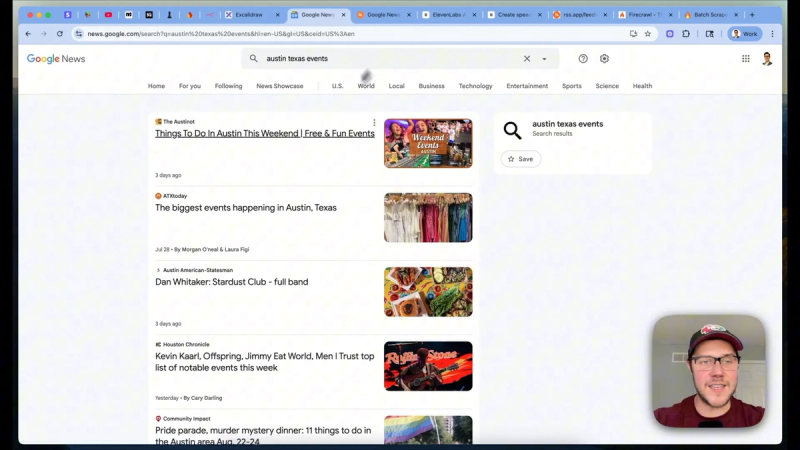
In n8n, create a simple workflow with a manual trigger. Add an HTTP request node that fetches the JSON feed URL you obtained. That request returns an array of items with titles and URLs. These links become the input for a batch scrape operation.
Key choices at this stage
- Keep your search narrow to avoid irrelevant results. Focus on city name plus event-related keywords.
- Limit the number of URLs per run to control scraping time and API billing.
- Store the JSON feed URL so you can reuse it for scheduled runs.
Step 2; Scrape full pages and normalize content
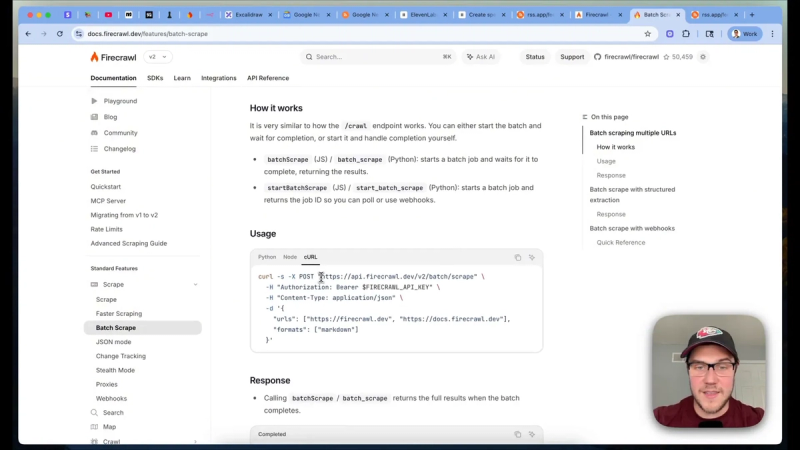
Once you have the list of article URLs, send them to a scraping service that returns cleaned Markdown for each page. I use Firecrawl’s batch scrape endpoint because it returns LLM-ready Markdown and metadata in one response. The API accepts an array of URLs and returns a job ID for a bulk operation.
After initiating a batch job, poll the Firecrawl status endpoint using the returned job ID. Implement a simple wait-and-retry loop in n8n. Wait for 15 seconds between polls and allow up to 30 retries. When the job status becomes completed, the response contains a data array with each scraped page in Markdown format and useful metadata.
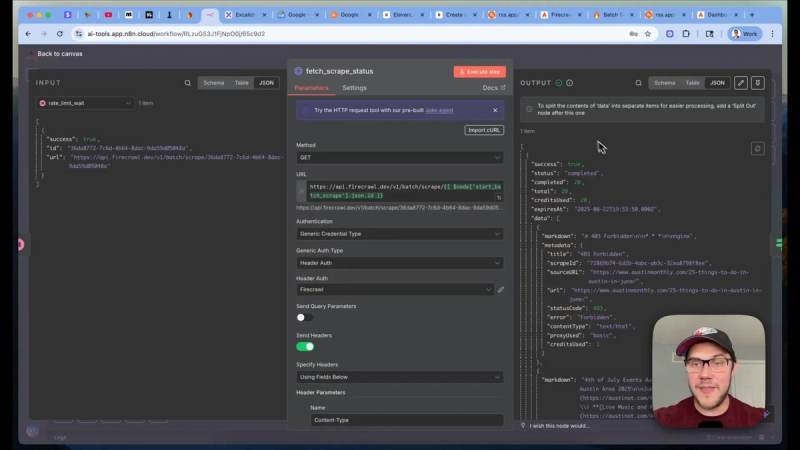
Practical tips
- Use a retry limit to avoid endless loops if a job stalls.
- Exclude images if you do not need them to speed up the scrape and reduce API cost.
- Consolidate the scraped pages into a single clean text field to simplify downstream prompts.
Step 3: Write the podcast script with audio tags
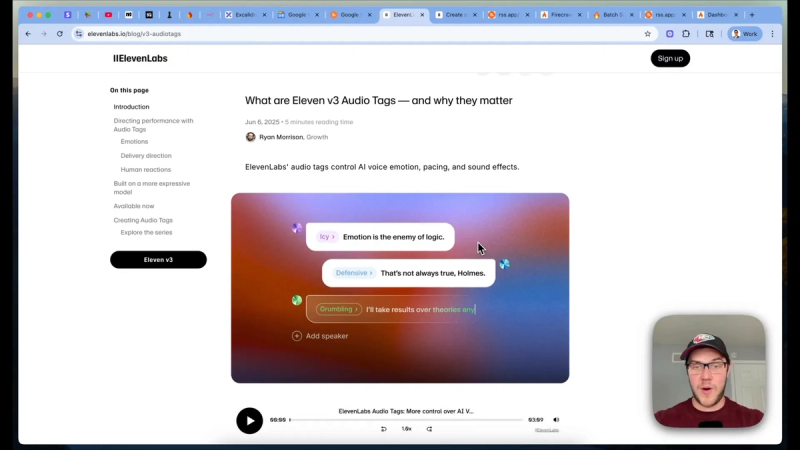
ElevenLabs v3 supports inline audio tags that control emotion, pacing, and sound effects. That capability lets you create a dynamic, human-feeling narration without manual audio editing. Feed the cleaned Markdown content into an LLM prompt that instructs it to write a short podcast script with tag usage guidelines attached.
Build your prompt with the following sections:
- Role and objective: explain this is a short city news brief for a local audience.
- Context: paste the scraped content and highlight which events to include.
- Tagging guide: include ElevenLabs v3 tag rules so the model understands how to place tags like [warmly], [excitedly], [chuckles], and [sfx: firework].
- Constraints: set an episode word limit, tone, and target audience.
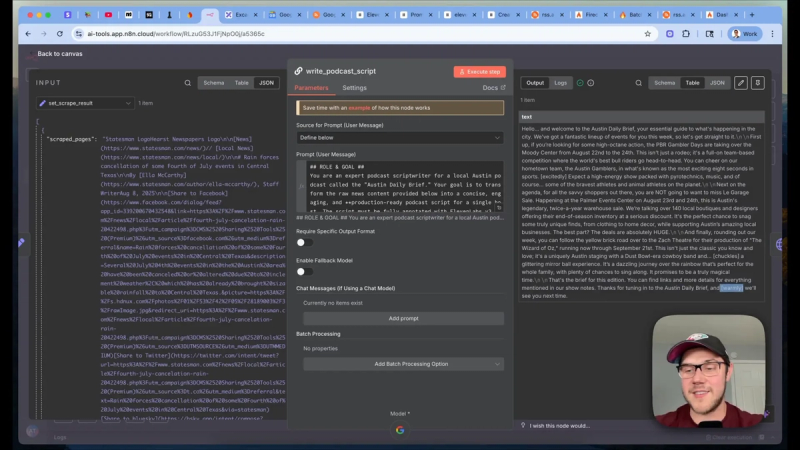
When you run the prompt, the LLM outputs a formatted script containing both text and inline audio tags. These tags control how the narrator will deliver each line and where sound effects occur. Keep the script brisk; a daily brief should be around one to three minutes.
Step 4: Generate the audio with ElevenLabs
With the tagged script in hand, call the ElevenLabs Text-to-Speech API to generate the final audio file. The request is a JSON body with two main fields: model set to Elevenv3 and text containing your tagged script. Choose a voice ID from the ElevenLabs library to match your brand.
Authentication requires an API key in the header. Use a credential node in n8n with header-based auth. Include the header name xi-api-key and paste your ElevenLabs API key as the value. Also set the output format if you want a specific bitrate, or rely on the default MP3 output.
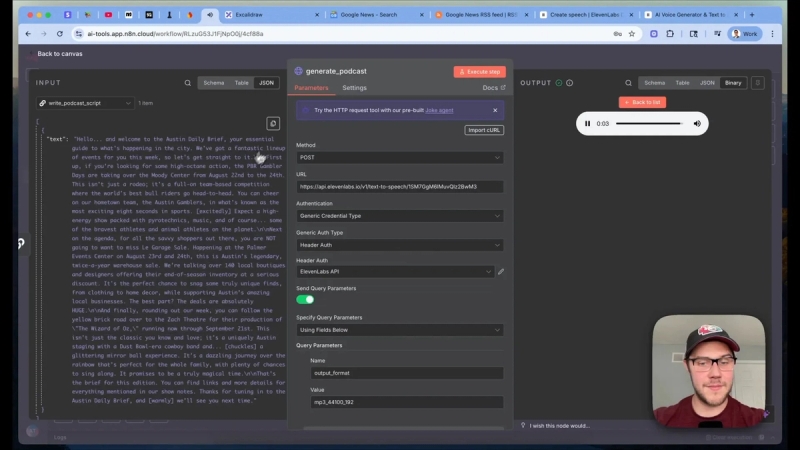
Submit the POST request. The API returns a data object with the audio file, which you can preview or store. You now have a fully generated episode narrated by the selected AI voice and decorated with expressive audio tags.
API parameters to consider
- output_format: default is fine for most uses, but specify if you need a particular bitrate.
- voice settings: adjust speed, stability, and style to tune the narration.
- language: set if you're producing non-English content.
Production and scaling notes
This base setup uses a single Google News query to create episodes. For production use, add more sources to increase coverage and reduce dependence on one feed. Consider a small data pipeline that ingests newsletters, community calendars, official city pages, and social posts. Store raw scraped material in a data lake so you can reprocess content for other formats like a newsletter or social audio clips.
Automate scheduling in n8n so episodes run at a fixed time each day. Add QA steps if you want human review before publishing. Add a publish node for hosting platforms or a CMS to post an episode and show notes automatically.
Safety and quality control
- Validate scraped content to avoid raw print errors, duplicate stories, or outdated events.
- Monitor voice output for mispronunciations and tune voice settings to improve naturalness.
- Keep an audit trail of inputs and outputs so you can review why a particular story was included.
Extend this system
Once the core automation works, expand in these directions:
- Multiple city feeds. Clone the workflow and change the initial search query to spin up local pods for other cities.
- Segmented episodes. Produce a short morning brief plus a longer weekend events edition by changing prompt constraints.
- Personalization. Use location or interest tags to customize episodes for different audience segments.
- Multilingual support. Use the language parameter with appropriate scraped sources to deliver non-English episodes.
Final checklist before you publish
- Confirm API keys for all services are stored securely in credentials.
- Run test episodes and listen for tag placement and natural pacing.
- Set sensible polling and retry parameters for batch scraping to avoid rate limits.
- Decide on a human review step if you want editorial control before release.
Conclusion
This system proves you can automate local audio content end to end using modern AI tools. Scrape event data, convert it into an LLM-ready format, instruct the model to build a tagged script, and synthesize human-feeling audio with ElevenLabs v3. With the template, you can scale to multiple markets and iterate on voice and format choices.
Join AI Automation Mastery to get the n8n template, the prompts, and community support to build your own AI-powered podcast network. Sign up and import the workflow to start customizing episodes for your city or niche.





